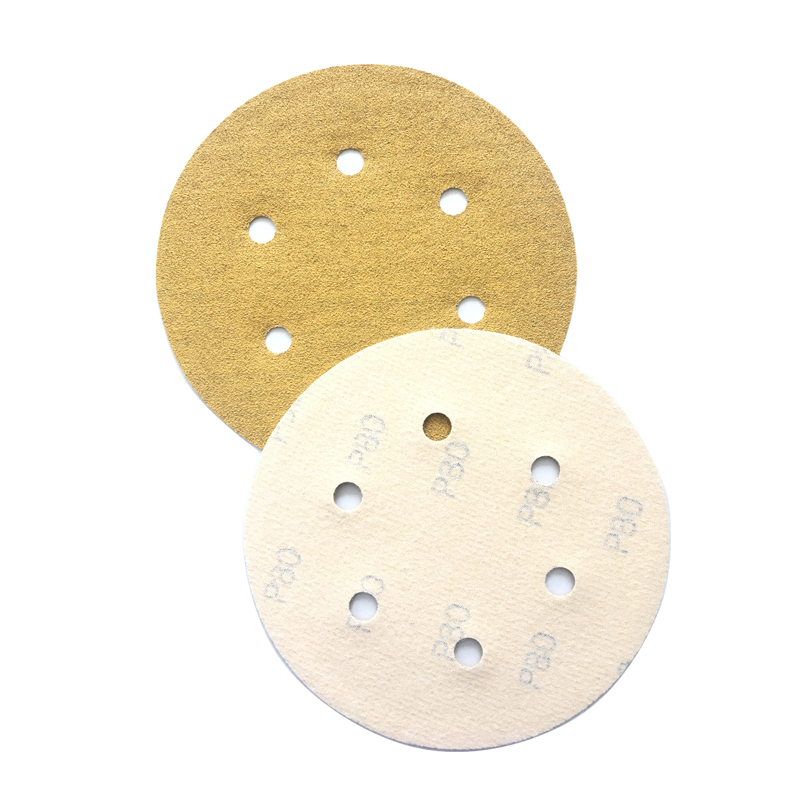
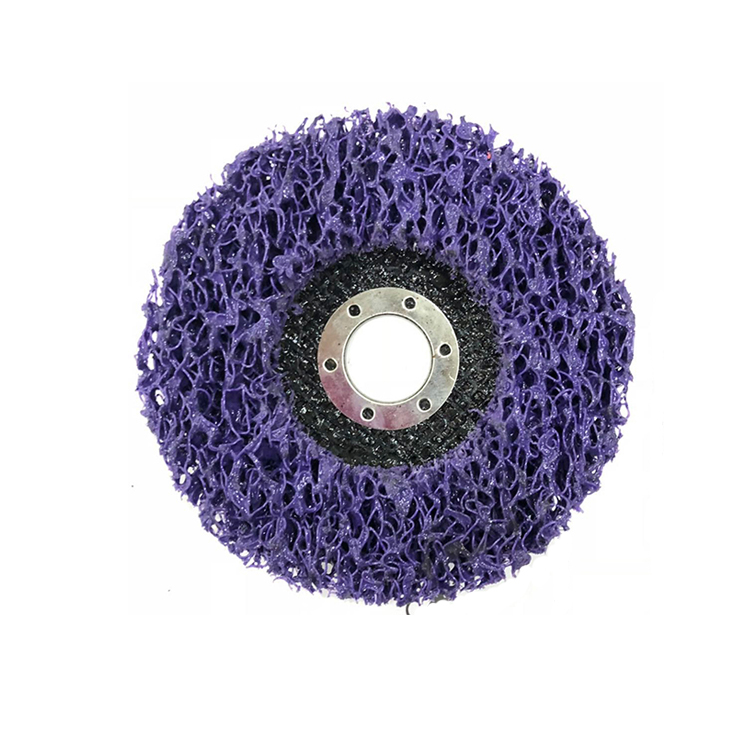
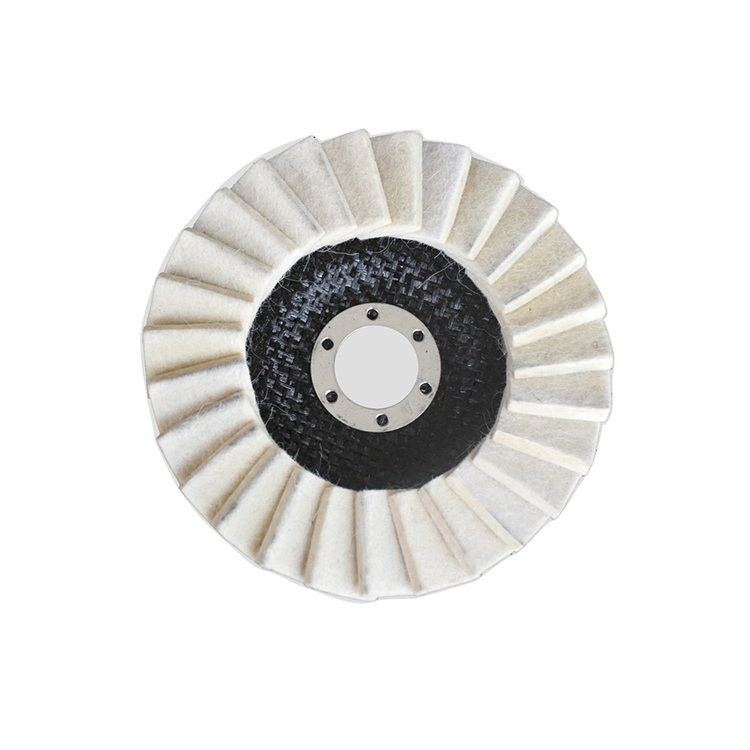
About laser cutting
2019-09-05 reading
About laser cutting
1 laser cutting principle
The laser is a kind of coherent light with high brightness, good directivity and good monochromaticity. The focused laser beam will produce tens of thousands of degrees of heat on any hard material. At this high temperature, any hard material will rapidly melt and evaporate instantaneously, and a very strong shock wave will be generated to explode and remove the molten material.
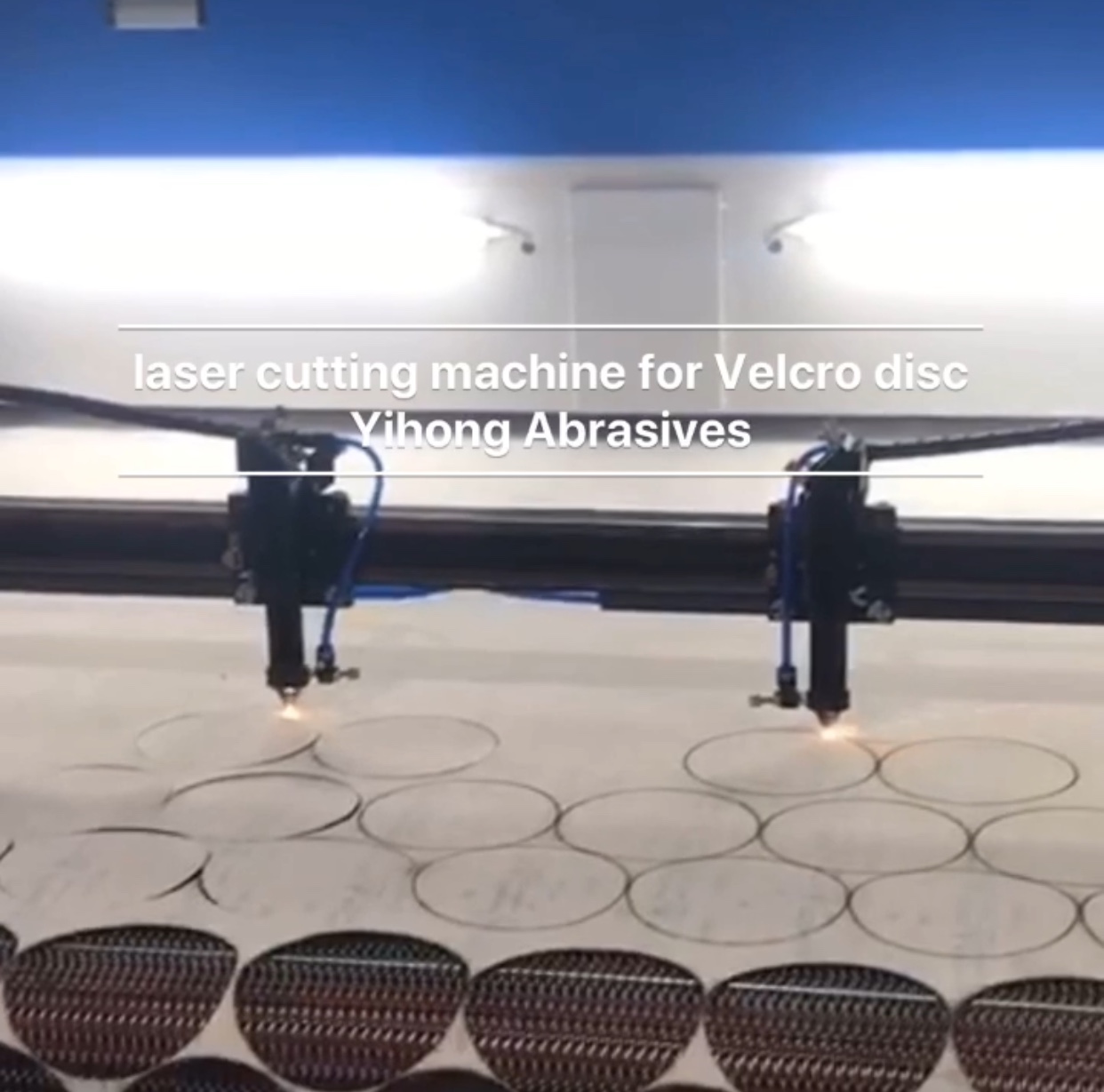

2 laser cutting classification
There are various classification standards for laser cutting. Generally, the laser cutting process is classified according to the principle of laser cutting and laser, and it can also be classified according to the composition structure, cutting material, working space and the like.
First, according to the principle of cutting, it can be divided into: vaporization cutting, high-pressure gas focusing melting cutting, oxidative melting cutting.
Vaporization cutting: Under the heating of high power density laser beam, the surface temperature of 0.5~6.0mm plate will rise rapidly to the boiling point temperature, which is enough to avoid the melting caused by heat conduction, so some materials are vaporized into steam and some materials are cut as the ejected material. The bottom of the slit is blown away by the auxiliary gas stream. The cutting gas is generally nitrogen or argon.
High-pressure gas focused fusion cutting: When the incident laser beam power density exceeds a certain value, the inside of the material at the beam irradiation point begins to evaporate, forming a hole that will absorb all the incident beam energy as a black body. The aperture is surrounded by the molten metal wall and then an auxiliary gas stream coaxial with the beam carries away the molten material around the hole. The cutting gas is generally nitrogen.
Oxidative melt cutting: Melting and cutting usually uses an inert gas, but if it is replaced by oxygen or other reactive gas, the material will be ignited under the irradiation of the laser beam, and a strong chemical reaction with oxygen will generate another heat source, namely oxidation. Melt cutting allows for higher cutting speeds. The cutting gas is generally oxygen.
Secondly, according to the classification of common lasers, it can be divided into: CO2 laser cutting, YAG laser cutting, fiber laser cutting.
CO2 laser cutting: used to cut thin metals, paper, wood, plastics, textiles and other non-metallic materials.
YAG laser cutting: can be used to cut metal, ceramic, plastic and graphite composites.
Fiber laser cutting: can be used to cut metal, ceramic, plastic and graphite composites. Not only does it provide the speed and cutting quality that CO2 laser cutting can achieve, but the maintenance and operating costs are low, which is the trend of laser cutting development in the future.